更新于2019.12.17 本文内容 Linux在线/离线安装Docker CE (开源版本) 鉴于公司一般使用Centos 7 作为服务器,本文只记录Centos 7系统. Docker pull centos After an image has been downloaded, you may then run a container using the downloaded image with the run subcommand. If an image has not been downloaded when docker is executed with the run subcommand, the Docker client will first download the image, then run a container using it: docker run centos. Index of linux/centos/7/x8664/./ edge/ nightly/ stable/ test/ edge/ nightly/ stable/ test/. Docker Compose is a tool used to define and run multi-container Docker applications. Users utilize this software to launch, execute, communicate, and close containers with a single coordinated command. This tutorial will show you how to install Docker Compose on CentOS 7. In this article. You can configure automatic log upload for continuous reports in Cloud App Security using a Docker on an on-premises Ubuntu, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), or CentOS server.
- Docker Centos Download Rpm
- Docker Download Centos Ubuntu
- Docker Download Centos Image
- Docker Ce Download Centos
As you download and use CentOS Linux, the CentOS Project invites you to be a part of the community as a contributor. There are many ways to contribute to the project, from documentation, QA, and testing to coding changes for SIGs, providing mirroring or hosting, and helping other users.
ISOs are also available via Torrent.
How to verify your iso
If you plan to create USB boot media, please read this first to avoid damage to your system.
If the above is not for you, alternative downloads might be.
The CentOS Linux 8 release notes and CentOS Stream release notes are continuously updated to include issues and incorporate feedback from users.
Cloud and container images
We build, maintain and update Cloud images that you can find on our Cloud Images server.
These images are built and made available for all the architectures that corresponding version supports.
People interested in importing ‘GenericCloud’ images into their own cloud solution can find corresponding images on the link above.
Worth knowing that you can also import (through Skopeo or other methods) container images the same way, and such .tar.xz files can be found on the same mirror.
Parallel to that, we have also official images that are available directly to be deployed for the following solutions:
If the above is not for you, alternative downloads might be.
Geographical mirrors
If you’re looking for a specific (or geographically local) mirror, please check out our list of current mirrors.
To check the status of a mirror, please visit mirror-status.centos.org.
Docker Centos Download Rpm
Sources
In order to help ease the workload for our primary mirror network, the sourcerpms are not kept in the same tree as the binary packages. If you need thesource packages used to build CentOS, you can find them in our vault vault.centos.org.
Older Versions
Legacy versions of CentOS are no longer supported. For historical purposes,CentOS keeps an archive of older versions. If you’re absolutely sure you needan older version then click here.
Export Regulations
By downloading CentOS software, you acknowledge that you understand all of thefollowing: CentOS software and technical information may be subject to the U.S.Export Administration Regulations (the “EAR”) and other U.S. and foreign lawsand may not be exported, re-exported or transferred (a) to any country listedin Country Group E:1 in Supplement No. 1 to part 740 of the EAR (currently,Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Sudan & Syria); (b) to any prohibited destination orto any end user who has been prohibited from participating in U.S. exporttransactions by any federal agency of the U.S. government; or (c) for use inconnection with the design, development or production of nuclear, chemical orbiological weapons, or rocket systems, space launch vehicles, or soundingrockets, or unmanned air vehicle systems. You may not download CentOS softwareor technical information if you are located in one of these countries orotherwise subject to these restrictions. You may not provide CentOS software ortechnical information to individuals or entities located in one of thesecountries or otherwise subject to these restrictions. You are also responsiblefor compliance with foreign law requirements applicable to the import, exportand use of CentOS software and technical information.
-->You can configure automatic log upload for continuous reports in Cloud App Security using a Docker on an on-premises Ubuntu, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), or CentOS server.
Prerequisites
OS:
- Ubuntu 14.04, 16.04, and 18.04
- RHEL 7.2 or higher
- CentOS 7.2 or higher
Disk space: 250 GB
CPU: 2
RAM: 4 GB
Set your firewall as described in Network requirements
Note
If you have an existing log collector and want to remove it before deploying it again, or if you simply want to remove it, run the following commands:
Log collector performance
The Log collector can successfully handle log capacity of up to 50 GB per hour. The main bottlenecks in the log collection process are:
Network bandwidth - Your network bandwidth determines the log upload speed.
I/O performance of the virtual machine - Determines the speed at which logs are written to the log collector's disk. The log collector has a built-in safety mechanism that monitors the rate at which logs arrive and compares it to the upload rate. In cases of congestion, the log collector starts to drop log files. If your setup typically exceeds 50 GB per hour, it's recommended that you split the traffic between multiple log collectors.
Set up and configuration
Step 1 – Web portal configuration: Define data sources and link them to a log collector
Go to the Automatic log upload settings page.
- In the Cloud App Security portal, click the settings icon followed by Log collectors.
For each firewall or proxy from which you want to upload logs, create a matching data source.
- Click Add data source.
- Name your proxy or firewall.
- Select the appliance from the Source list. If you select Custom log format to work with a network appliance that isn't listed, see Working with the custom log parser for configuration instructions.
- Compare your log with the sample of the expected log format. If your log file format doesn't match this sample, you should add your data source as Other.
- Set the Receiver type to either FTP, FTPS, Syslog – UDP, or Syslog – TCP, or Syslog – TLS.
Note
Integrating with secure transfer protocols (FTPS and Syslog – TLS) often requires additional settings or your firewall/proxy.
f. Repeat this process for each firewall and proxy whose logs can be used to detect traffic on your network. It's recommended to set up a dedicated data source per network device to enable you to:
- Monitor the status of each device separately, for investigation purposes.
- Explore Shadow IT Discovery per device, if each device is used by a different user segment.
- Click Add data source.
Go to the Log collectors tab at the top.
- Click Add log collector.
- Give the log collector a name.
- Enter the Host IP address of the machine you'll use to deploy the Docker. The host IP address can be replaced with the machine name, if there is a DNS server (or equivalent) that will resolve the host name.
- Select all Data sources that you want to connect to the collector, and click Update to save the configuration.
Further deployment information will appear. Copy the run command from the dialog. You can use the copy to clipboard icon.
Export the expected data source configuration. This configuration describes how you should set the log export in your appliances.
Note
- A single Log collector can handle multiple data sources.
- Copy the contents of the screen because you will need the information when you configure the Log Collector to communicate with Cloud App Security. If you selected Syslog, this information will include information about which port the Syslog listener is listening on.
- For users sending log data via FTP for the first time, we recommend changing the password for the FTP user. For more information, see Changing the FTP password.
Step 2 – On-premises deployment of your machine

The following steps describe the deployment in Ubuntu.
Note
The deployment steps for other supported platforms may be slightly different.
Open a terminal on your Ubuntu machine.
Change to root privileges using the command:
sudo -iTo bypass a proxy in your network, run the following two commands:
If you accept the software license terms, uninstall old versions and install Docker CE by running the commands appropriate for your environment:
Remove old versions of Docker:
yum erase docker docker-engine docker.ioInstall Docker engine prerequisites:
yum install -y yum-utilsAdd Docker repository:
Install Docker engine:
yum -y install docker-ceStart Docker
Test Docker installation:
docker run hello-world
Remove old versions of Docker:
yum erase docker docker-engine docker.ioInstall Docker engine prerequisites:
Add Docker repository:
Install dependencies:
Install Docker engine:
sudo yum install docker-ceStart Docker
Test Docker installation:
docker run hello-world
Remove the container-tools module:
yum module remove container-toolsAdd the Docker CE repository:
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repoModify the yum repo file to use CentOS 8/RHEL 8 packages:
sed -i s/7/8/g /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repoInstall Docker CE:
yum install docker-ceStart Docker
Test Docker installation:
docker run hello-world
Remove old versions of Docker:
apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.ioIf you are installing on Ubuntu 14.04, install the linux-image-extra package.
Install Docker engine prerequisites:
Verify that the apt-key fingerprint UID is docker@docker.com:
apt-key fingerprint | grep uidInstall Docker engine:
Test Docker installation:
docker run hello-world
Deploy the collector image on the hosting machine by importing the collector configuration. Import the configuration by copying the run command generated in the portal. If you need to configure a proxy, add the proxy IP address and port number. For example, if your proxy details are 192.168.10.1:8080, your updated run command is:
Verify that the collector is running properly with the following command:
docker logs <collector_name>
You should see the message: Finished successfully!
Step 3 - On-premises configuration of your network appliances
Configure your network firewalls and proxies to periodically export logs to the dedicated Syslog port or the FTP directory according to the directions in the dialog. For example:
Step 4 - Verify the successful deployment in the Cloud App Security portal
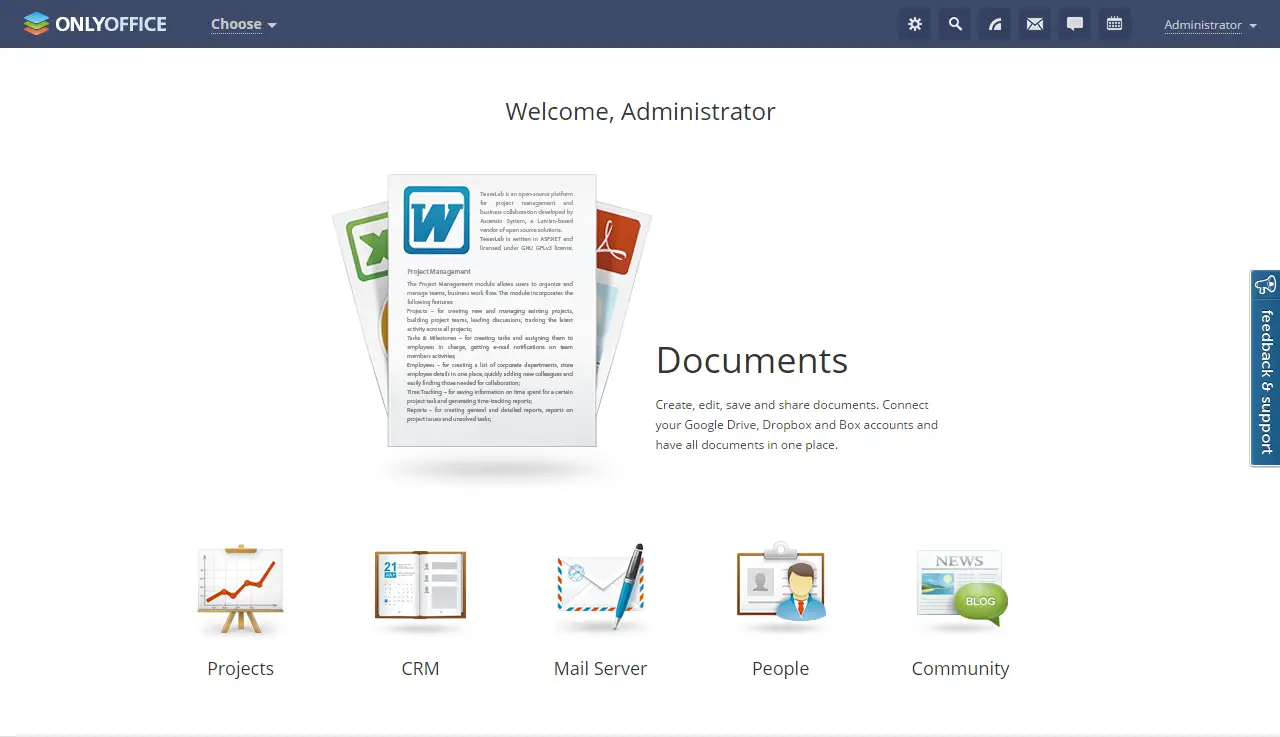
Check the collector status in the Log collector table and make sure the status is Connected. If it's Created, it's possible the log collector connection and parsing haven't completed.
You can also go to the Governance log and verify that logs are being periodically uploaded to the portal.
Docker Download Centos Ubuntu
Alternatively, you can check the log collector status from within the docker container using the following commands:
- Log in to the container by using this command:
docker exec -it <Container Name> bash - Verify the log collector status using this command:
collector_status -p
Docker Download Centos Image
If you have problems during deployment, see Troubleshooting Cloud Discovery.
Optional - Create custom continuous reports
Verify that the logs are being uploaded to Cloud App Security and that reports are generated. After verification, create custom reports. You can create custom discovery reports based on Azure Active Directory user groups. For example, if you want to see the cloud use of your marketing department, import the marketing group using the import user group feature. Then create a custom report for this group. You can also customize a report based on IP address tag or IP address ranges.
- In the Cloud App Security portal, under the Settings cog, select Cloud Discovery settings, and then select Continuous reports.
- Click the Create report button and fill in the fields.
- Under the Filters you can filter the data by data source, by imported user group, or by IP address tags and ranges.

Next steps
Docker Ce Download Centos
If you run into any problems, we're here to help. To get assistance or support for your product issue, please open a support ticket.
