Step by Step Tutorial on How to Install Docker Compose on Ubuntu 18.04. Also, learn to create and manage new containers using Docker Compose applications. Docker Desktop includes Docker App, developer tools, Kubernetes and version synchronization to production Docker Engines. Docker Desktop allows you to leverage certified images and templates and your choice of languages and tools. Development workflows leverage Docker Hub to extend your development environment to a secure repository for rapid.
Estimated reading time: 3 minutes
Docker Desktop for Mac is the Community version of Docker for Mac.You can download Docker Desktop for Mac from Docker Hub.
By downloading Docker Desktop, you agree to the terms of the Docker Software End User License Agreement and the Docker Data Processing Agreement.
System requirements
Your Mac must meet the following requirements to successfully install Docker Desktop:
macOS must be version 10.14 or newer. That is, Mojave, Catalina, or Big Sur. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of macOS.
If you experience any issues after upgrading your macOS to version 10.15, you must install the latest version of Docker Desktop to be compatible with this version of macOS.
Note
Docker supports Docker Desktop on the most recent versions of macOS. That is, the current release of macOS and the previous two releases. As new major versions of macOS are made generally available, Docker stops supporting the oldest version and supports the newest version of macOS (in addition to the previous two releases). Docker Desktop currently supports macOS Mojave, macOS Catalina, and macOS Big Sur.
At least 4 GB of RAM.
VirtualBox prior to version 4.3.30 must not be installed as it is not compatible with Docker Desktop.
What’s included in the installer
The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Notary, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper.
Install and run Docker Desktop on Mac
Double-click
Docker.dmgto open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder.Double-click
Docker.appin the Applications folder to start Docker. (In the example below, the Applications folder is in “grid” view mode.)The Docker menu in the top status bar indicates that Docker Desktop is running, and accessible from a terminal.
If you’ve just installed the app, Docker Desktop launches the onboarding tutorial. The tutorial includes a simple exercise to build an example Docker image, run it as a container, push and save the image to Docker Hub.
Click the Docker menu () to seePreferences and other options.
Select About Docker to verify that you have the latest version.
Congratulations! You are now successfully running Docker Desktop.
If you would like to rerun the tutorial, go to the Docker Desktop menu and select Learn.
Automatic updates
Starting with Docker Desktop 3.0.0, updates to Docker Desktop will be available automatically as delta updates from the previous version.
When an update is available, Docker Desktop automatically downloads it to your machine and displays an icon to indicate the availability of a newer version. All you need to do now is to click Update and restart from the Docker menu. This installs the latest update and restarts Docker Desktop for the changes to take effect.
Uninstall Docker Desktop
To uninstall Docker Desktop from your Mac:

- From the Docker menu, select Troubleshoot and then select Uninstall.
- Click Uninstall to confirm your selection.
Important
Uninstalling Docker Desktop destroys Docker containers, images, volumes, andother Docker related data local to the machine, and removes the files generatedby the application. Refer to the back up and restore datasection to learn how to preserve important data before uninstalling.
Where to go next
- Getting started provides an overview of Docker Desktop on Mac, basic Docker command examples, how to get help or give feedback, and links to other topics about Docker Desktop on Mac.
- Troubleshooting describes common problems, workarounds, howto run and submit diagnostics, and submit issues.
- FAQs provide answers to frequently asked questions.
- Release notes lists component updates, new features, and improvements associated with Docker Desktop releases.
- Get started with Docker provides a general Docker tutorial.
- Back up and restore data provides instructionson backing up and restoring data related to Docker.
Docker Install Download Free
mac, install, download, run, docker, localInstalling Docker on Ubuntu is simple because Ubuntu provides Docker in its repositories. However, Docker is not available in CentOS's default repositories.
Fret not, there are three ways you can install docker on a CentOS Linux system.
- Using docker's repository
- Downloading the RPM
- Using helper scripts
Here, I'll walk you through the installation process of Docker CE using docker's RPM repository.
Docker CE stands for Docker Community Edition. This is the free and open source version of Docker. There is Docker EE (Enterprise Edition) with paid support. Most of the world uses Docker CE and it is often considered synonymous to Docker.
Installing Docker on CentOS
Before going any further, make sure you have the system updated. You can update the CentOS using:
Step 1: Add the official repository
Add docker's official repository using the following command
You should also update the package cache after adding a new repository:
Step 2: Install Docker CE
The trouble with using a custom repository is that it may have dependency issue if you try installing the latest version of docker-ce.
For example, when I check the available versions of docker-ce with this command:
I got docker-ce-3:19.03.9-3.el7 as the latest version. But the problem in installing the latest version is that it depends on containerd.io version >=1.2.2-3. Now, this version of containerd.io is not available in CentOS 8.
To avoid this dependency cycle and battling them manually, you can use the --nobest option of the dnf command.
It will check the latest version of docker-ce but when it finds the dependency issue, it checks the next available version of docker-ce. Basically, it helps you automatically install the most suitable package version with all the dependencies satisfied.
To install docker in CentOS without getting a migraine, try this command and see the magic unfold on your terminal screen:
You'll be prompted to import a GPG key, make sure the key matches to 060A 61C5 1B55 8A7F 742B 77AA C52F EB6B 621E 9F35 before entering 'y'.
containerd.io is a daemon for managing containers. Docker is just one form of Linux containers. To make the various types of container images portable, Open Container Initiative has defined some standards. containerd is used for managing the container images conforming to OCI standard.
Setting up docker on CentOS
Docker Install Download Windows 10
Alright! You have docker installed but it's not yet ready to be used yet. You'll have to do some basic configurations before it can be used smoothly.
Run docker without sudo
You can run docker without any sudo privileges by adding your user to the docker group.
The docker group should already exist. Check that using the following command:
If this outputs nothing, create the docker group using groupadd command like this:
Now add your user to the docker group using the usermod command:
Change the user_name in the above command with the intended user name.
Now log out and log back in for the group change to take effect.
Start docker daemon
Docker is installed. Your user has been added to the docker group. But that's not enough to run docker yet.
Before you can run any container, the docker daemon needs to be running. The docker daemon is the program that manages all the containers, volumes, networks etc. In other words, the daemon does all the heavy lifting.

Start the docker daemon using:
You can also enable docker daemon to start automatically at boot time:
Verify docker installation by running a sample container
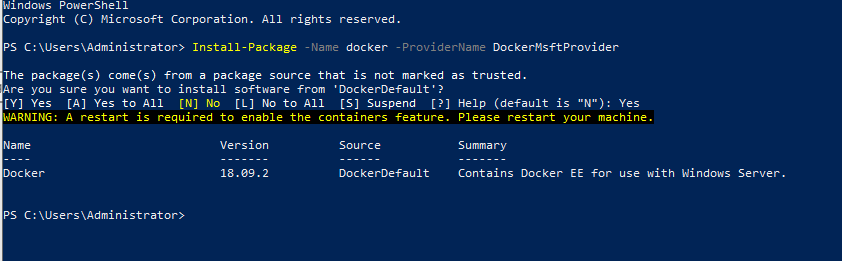
Everything is done. It's time to test whether the installation was successful or not by running a docker container.
To verify, you can run the cliché hello-world docker container. It is a tiny docker image and perfect for quickly testing a docker installation.
If everything is fine, you should see an output like this:
Here's what the command is doing behind the hood:
- The docker client, i.e. the command line tool that you just used, contacted the docker daemon.
- The daemon looked for hello-world docker image in the local system. Since it doesn't find the image, it pulls it from Docker Hub.
- The engine creates the container with all the options you provided through the client's command line options.
This hello-world image is used just for testing a docker installation. If you want a more useful container, you can try running Nginx server in a container like this:
Once the command is done running, open up a browser and go to http://your_ip_address:56788. I hope you know how to know your IP address in Linux.
You should see nginx server running. You can stop the container now.
I hope this tutorial helped you in installing docker on CentOS. Do subscribe for more Docker tutorials and DevOps tips.
Become a Member for FREE
Join the conversation.
